How often should the water in the aquarium be changed and how should it be done?

The aquarium is an interior decoration, at the same time humidifies the air in the room and contributes to the emotional relaxation of the owner after a busy day.
Many cafes and shopping centers use beautiful aqua systems to attract visitors, because you can watch the fish for hours. Sometimes aquariums are located in the offices of bosses and directors, because watching the fish, as well as caring for the aquarium, is great for reducing stress and improving mood.
Partial water changes not only help maintain aesthetics and beauty, but also have a beneficial effect on the health of the inhabitants of the aquarium.



What is it for?
An aquarium is a closed ecosystem with its own biobalance, turbidity or other pollution of the water indicates a violation of the delicate balance. Cloudy or acidic water adversely affects fish, slows down plant growth and can lead to disease and even death of the entire ecosystem in the aquarium.
Important is regular fluid changes, it helps maintain a normal nitrogen cycle. A special filter and aerator helps to keep the aquarium water clean, but regular partial changes, additional cleaning of the bottom of the aquarium and removing plaque from the walls are very important conditions for keeping the water clean.
A complete fluid change should only be carried out if absolutely necessary, as it is stressful for the inhabitants, and the microclimate after such a restart is built anew.
In dirty water, fish reproduce poorly, begin to hurt and die.Especially bad water affects expensive fish species, as they are artificially bred and have fragile health.

What affects the frequency of replacement?
It is not necessary to change the water in the aquarium very often and it is not difficult to do it.
Aquarists disagree on only one thing: you should change the water completely or leave the ¼ "old" liquid (after cleaning it) for the best and faster restoration of the microclimate after general cleaning. If the plants or fish are sick, it is necessary to quarantine them in an empty container without decor, rinse everything thoroughly and completely change the water.
Correct water changes will help avoid general cleaning for as long as possible.
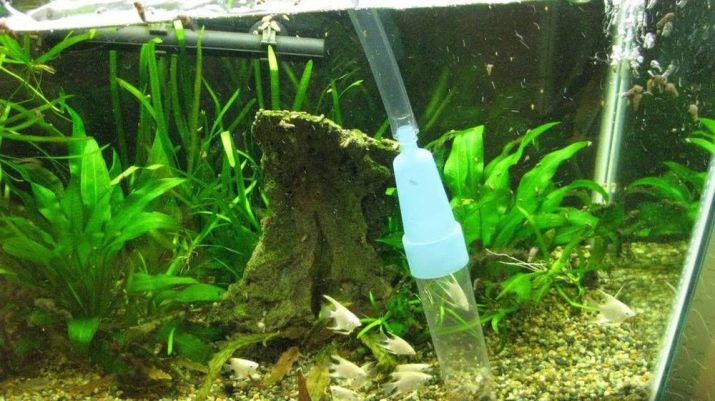

If the container has a volume of 60 liters to 100 liters, it is recommended to change the fluid according to the schedule:
- 1 time in 2-3 weeks, clean the bottom and add water to the usual level;
- once a month and a half, clean the walls, the bottom, rinse the filter filler, clean the decorative elements with a brush (if there is a bloom of brown / green microalgae on them) and renew 1/4 of the liquid in the aquarium;
- about once a year (or less often), carry out a full general cleaning: place the fish in a separate container with clean water, thoroughly wash the entire aquarium, plants and decorative elements (in this case, ¼ "old" aquarium liquid must be passed through cheesecloth folded in 3 layer and add to a clean aquarium).
A small aqua system is too troublesome, despite the widespread PR of 10-liter tanks, they are hopeless, suitable for keeping 1-2 fish (or growing fry) with the condition of weekly cleaning the bottom and glass, as well as replacing a quarter of the water. The liquid in such aquariums constantly turns sour, blooms and becomes cloudy.

A large aquarium (from 300 liters or more) needs to change the liquid much less often, the main thing is to correctly populate it and arrange it at the first start. If the water becomes quickly and intensively contaminated, it is necessary to find the cause and eliminate it. Possible reasons for the rapid turbidity or blooming of water include the following:
- too small aquarium capacity (10 liters);
- the aqua system is installed near a window on the sunny side of the house and the water blooms profusely;
- overcrowding of the aquarium (1 liter of liquid is needed for 1 fish of 3 cm in size, 8-10 liters for a fish of 10 cm);
- there is no filter in the aquarium or it is faulty;
- high temperature conditions provoke acidification of the liquid;
- the presence of snails, especially large species (despite the generally accepted opinion that snails clean the walls, the amount of their excrement is twice the benefit from cleaning glass);
- the use of low-quality soil;
- a thick layer of duckweed on the surface of the water creates a waterlogging effect;
- overfeeding fish and subsidence of a part of dry or live food to the bottom;
- feeding fish with bread crumbs or raw scraped meat;
- poor quality of the water itself (for example, with a high content of iron or lime);
- the use of low-quality plant weights;
- using ordinary river sand as a cover on the bottom (it cannot be cleaned, fish often dig such a bottom and raise the sand).
Ideally, with proper aquarium care and maintenance, the water should remain clear and odor-free for several years.

Optimal timing
Before the first start-up, all walls in a new aquarium should be rinsed with baking soda and rinsed thoroughly. After installation in the desired place, pour settled tap water, fill with decorative elements and let stand for 2-3 days. If the water remains clear and clear, you can start the fish.
The number of inhabitants, plants and food must be carefully calculated and these data must always be kept at hand until they become a habit. Even the most unpretentious fish should not overpopulate the aquarium.Excess individuals can be sold or given away, as well as plants, because some grow very quickly.
Excess feed has a negative effect on the digestive system of the fish and contributes to the very rapid cloudiness of the water.
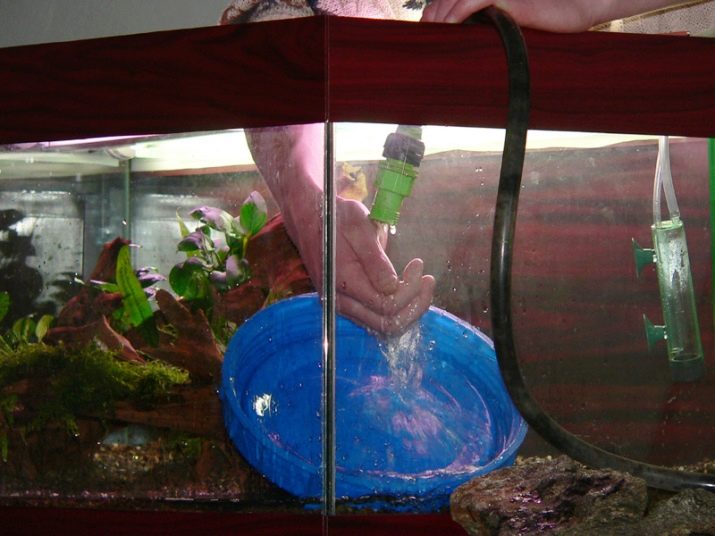

You need to change the liquid almost completely no more than once a year for aquariums from 30 to 50 liters, the rest of the time, only a partial change of the water should be done, which decreases during the harvesting process and due to natural evaporation. Frequent fluid changes disrupt the microclimate in the aquarium and adversely affect its inhabitants.
It is more difficult to maintain cleanliness and biological balance in tanks with a capacity of 20 liters than in large ones, but it is recommended to make a fluid change no more than 1 time per week. For beginner aquarists, it is better to buy a container of at least 40 liters in volume to facilitate the maintenance of the ecosystem.
After the first start, it is advisable not to add water for two months in order to establish a biological balance, but it is necessary to clean the bottom and walls regularly.
The first change in a new aquarium should be no more than 10 percent of the total tank volume.
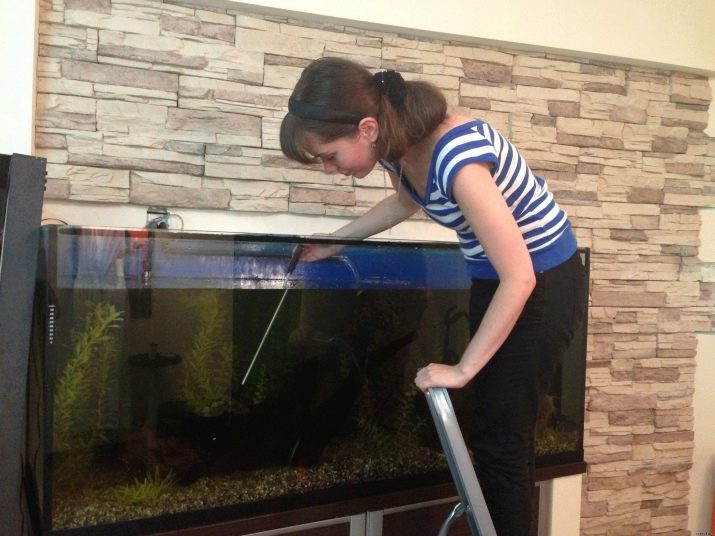

In large aquariums with a capacity of more than 100-200 liters, the task of keeping the ecosystem clean is greatly simplified. A container of such a volume will become dirty for much longer, the bottom can be cleaned once every 3 weeks. Water should be topped up as needed (you must first let it settle for several days). If a sediment forms in the settled liquid, it is necessary to pour it out not completely so that the settled particles do not get to the fish.

Required inventory
Before carrying out a water change, it should be allowed to settle in a clean glass jar covered with gauze (fixed with an ordinary rubber band around the perimeter of the neck) for 5-7 days. You cannot boil water for fish, since the boiling process kills oxygen and beneficial bacteria (such water is useless and is considered inanimate).
In order to facilitate the procedure of changing or replacing the liquid in the aquarium, it is recommended to use the following tools:
- glass scraper or piece of gauze;
- a net for fish;
- scissors for thinning out excess plants (remove the roots from the soil very carefully so as not to damage the plant and not pick up dirt from the bottom);
- a container for extra fish and plants (it is advisable to use a clean glass jar);
- a siphon with a pear or an ordinary tube plus a hose for cleaning the soil;
- a bucket for the drained dirty liquid.
We recommend using a hose that is at least 1.5 m long. You may also need filter media if you plan to clean it.


In the process of changing the water, you can catch the existing fry with a net with a fine mesh, if you plan to grow them (before that, you need to read when the young growth can be deposited, these periods differ for different types of fish).
If there are many plants in the aquarium, you can use special diffuser for atomizing carbon dioxide. It is convenient to thin out plants with tweezers, but it is not necessary to use them.
In the process of breeding expensive fish breeds, you can use special tests for water, which help to accurately determine the composition of the liquid and make sure that a liquid change is necessary.
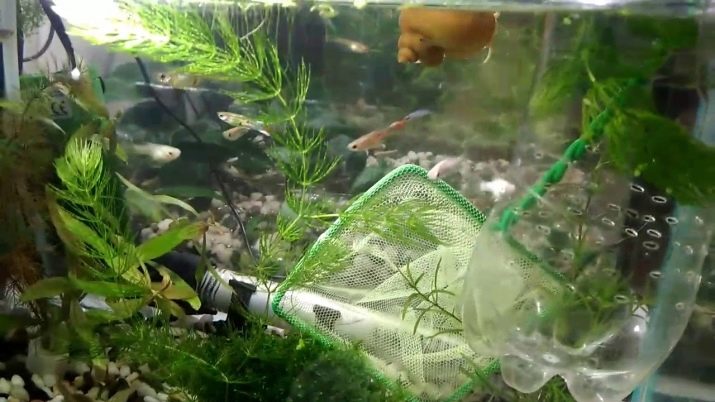

Procedure rules
The age of the aquarium affects the frequency of fluid changes. A new aquarium is considered the first 2 months after launch, and it is not recommended to touch the water in it. Young is considered from 2 to 3 months, and fluid change should be no more than 1/5 of the total volume, no more than 1 time in 2 weeks. Mature aquarium - 3 to 6 months, water change - once a week. The aquarium becomes old by the age of two and requires a change of the minimum amount of water that decreases during the cleaning process (no more than 1/6 of the total volume).
It is recommended to carry out a partial water change according to the following algorithm (you do not need to set the fish, it is enough to be careful):
- clean the walls of the aquarium with a special scraper or piece of gauze from green / brown deposits;
- remove fallen leaves of plants, excess duckweed;
- place extra fish, snails and plants in a separate container in order to sell or give them away (or exchange them for food and other necessary things);
- clean the bottom of the waste products of the inhabitants of the aquarium and food residues using a special tube with a hose;
- wash your hands thoroughly (you can use a clear, odorless detergent for washing baby dishes for this);
- remove edge-of-water deposits from the glass with a piece of gauze;
- if the water is cloudy, drain a quarter of the tank volume through a hose;
- add settled clean water to the usual level.



A complete water change is rare and takes longer than a partial water change. The rules for a complete water change (such a replacement must be combined with general cleaning of the aquarium, simple draining / topping up of water will have no effect and after a couple of days the water will become cloudy):
- fish and snails must be deposited in a separate container with clean water;
- the plants should be placed in a basin of water, rinsed thoroughly, the clutches of snails (if they are not needed) and microalgae plaque removed (very carefully, with gauze);
- all decorative elements should be thoroughly washed with a hard new toothbrush (you can use baking soda, but then rinse thoroughly under running water);
- all water should be bled out or drained through a hose;
- the aquarium must be washed with baking soda and rinsed very thoroughly;
- the soil should be rinsed under a high pressure of water from the shower;
- fill the aquarium by a third with clean water;
- equip the bottom, distribute the decor, fix the aerator, filter, heater;
- plant plants and carefully mask their roots;
- put a clean deep plate on the bottom and slowly add water to the usual level in a thin stream;
- after an hour, you can run all the inhabitants back into the aquarium.


It is not difficult to completely change the water in an aquarium of any capacity, but this should be done only if absolutely necessary. Correct and regular replacement of aquarium water guarantees the maintenance of a healthy microclimate, has a beneficial effect on the health of its inhabitants and gives aesthetic pleasure to its owner.
How to change the water in the aquarium is shown in the next video.