How long do aquarium fish live?

For a beginner who is looking for inhabitants for his aquarium for the first time, it is important that his pets live as long as possible. Due to inexperience, you can chase external beauty and purchase a copy that will live on the strength of 1.5 years. To make the choice conscious, it is worth getting to know the types of aquarium fish and learn about the features of their maintenance.

How to determine the age of aquarium fish?
Make sure that there are young fish swimming in your pet store aquarium immediately before buying. It is easy to find out: the young are actively moving, they have shiny scales, their eyes are clean without clouding.
Old or sick fish are either inactive or lie at the bottom of the aquarium. However, in some species, signs of aging appear shortly before death. For example, thorns become discolored, individual scales fall out in barbs, and fins in macropods sag.

Then you should pay attention to the color. As a rule, fry are paler in comparison with bright saturated color of adults. For example, in swordsmen, the color is formed during the first months of life and at the age of six months the fish has a beautiful color.
Goldfish fry are greenish-bronze in color and have a rounded tail fin. Young ancistrus catfish are sold without the characteristic antennae on the muzzle - they appear in males after a year.
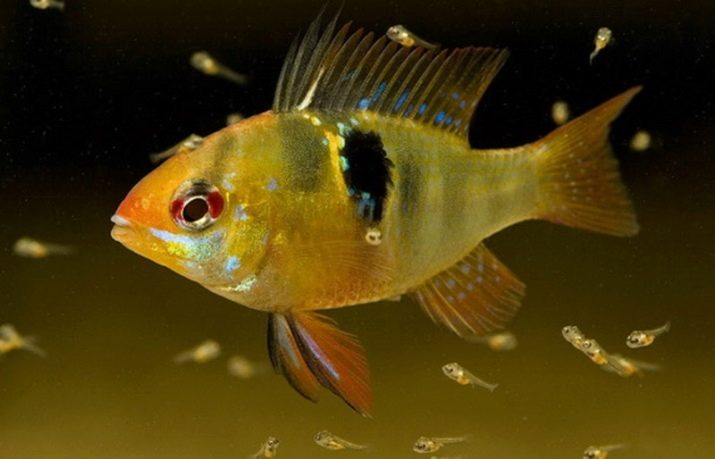

Juveniles are much smaller than adults of the underwater world. It is important to ask the seller about the conditions in which the fish were kept. After all, a small size may indicate poor conditions for keeping fish and a lack of food.
Life span of different breeds
At home, aquarium fish can live from a year to 15 years. This often depends on the size of a particular species: small fish live shorter, larger species have more vitality.
Life expectancy can only be calculated for a specific species. This does not require the tedious compilation of special tables - it is enough to summarize the available data.
For example, tetra, neon and lalius can live from 4 to 6 years. The rest of the miniature species such as guppies, iris, pecelia, mollies, wedge-bellies and cetradon live no more than 5 years.

The life span of the larger piranha, pacu, cardinal, sturizome and balu shark is up to 10 years. Macropod dies at age 7, glass catfish at age 8 and loach at age 9.
A similar upper bar for frontosa, cichlamosa, black morulis, botsia, plekostomus and barbus. Severum is a kind of long-liver - with proper care and ideal conditions, this fish can live up to 18 years.

It was no coincidence that leaving was mentioned, because without observing the rules for keeping fish, they will not delight with their beauty and smooth movements. Therefore, a novice aquarist should familiarize himself with the conditions that he has to create for future pets.
What factors affect the life span?
The life expectancy of fish is significantly influenced by their sex. Males live much longer than females (especially in viviparous breeds). Females often die from exhaustion during pregnancy or after unsuccessful spawning. The difference in life expectancy for any species is approximately 1-2 years.
In addition to sex differences, experts identify a number of factors that affect the longevity of aquarium fish. Novice aquarists should familiarize themselves with them in more detail.
Water temperature and condition
An important condition is the temperature of the water in the aquarium. Some species are sensitive to the slightest temperature fluctuations. Even a deviation of 1-2 degrees can lead to illness and death of the pet.
The fish have no own thermoregulation at all, therefore metabolic processes in their body are directly related to the temperature of the water. - the higher its temperature, the higher their metabolic rate.
It has long been noted that warm-water breeds live less than their counterparts, which prefer cooler conditions. All varieties of goldfish are such long-livers. At the same time, experienced breeders note that in addition to the love of cold water, these breeds are distinguished by their peaceful nature, which makes them good neighbors.

Another important factor is the condition of the water. The liquid must meet the requirements of a particular species, so before buying it is worth making sure that only warm or cold-loving species will settle in the aquarium.
It is necessary to take into account the preferences of the selected breed for the acidity and hardness of the water, as well as observe the temperature conditions. For example, discus and scalars require the water temperature to be at least 25-31 degrees, acidity - 5.5-6.5 Ph and hardness - 1-4 units.
For viviparous fish, the acidity of the water should be 7-8.5 Ph with a hardness of 15-25 and a temperature of 23-28 degrees. For labyrinths, these indicators are 6.5-6.7, 5-10, 23-28, respectively.
The hardness and acidity of water is determined using special tests, the temperature is controlled using a thermometer. Aquarium fish easily adapt to the proposed conditions, but most species require moderately hard water. A breeds such as barbs, cockerels and neons are only suitable for soft water.


Among other things, the aquarium needs regular cleaning, since dirty water is toxic, pathogenic bacteria develop in it, which have a detrimental effect on the condition of the fish. Therefore, a compressor and a filter for water purification should be mandatory attributes of the aquarium.And once a week, a third of the main volume should be replaced with clean, settled water.

Correct neighborhood
Correctly selected breeds have a significant impact on the life expectancy of the inhabitants of the aquarium. For example, aggressive males get along well with phlegmatic catfish and calm tetras, macrognathus, cules, swordtails.
All types of goldfish get along well with each other, but it is better not to let small representatives of the aquarium fauna come to them. Goldfish are omnivorous, are in constant search of food and can eat their neighbors. Neighborhood with a taracatum or a corridor is allowed.
Together with small guppies, battles, neons, as well as blue, white, diamond, green-striped and lemon tetras will get along. Good neighbors for barbs will be swordsmen, zebrafish, botia and gourami.


Carnivorous cichlids do not differ in hospitality, but they get along well in the same aquarium with catfish, battles and gourami (especially if they grew up together). Black-striped cichlids, astronotus, discus, mileus, red hemihromis coexist with piranhas.
As neighbors for these predators, two types of cichlazomas are also suitable - meek and severum. Any other species will be perceived by these dangerous beauties as prey, so you should not experiment with hooking.
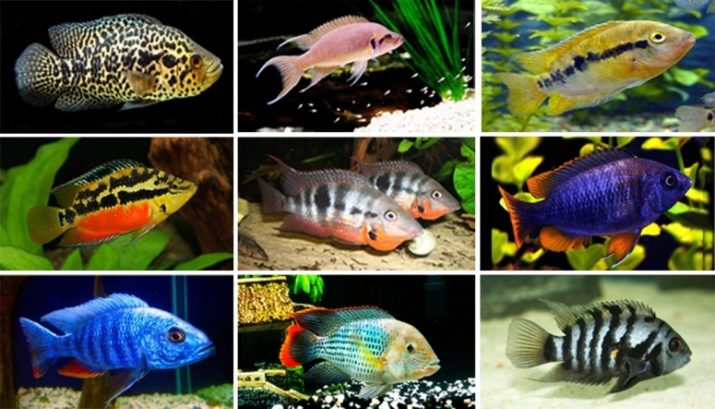

Experienced breeders say it's not enough to find compatible fish breeds. You need to provide your pets with shelter in the form of grottoes or densely planted algae, in which they can hide and rest.

It is important to avoid overpopulation of the aquarium - if several large flocks live in a small container at once, the fish will constantly experience stress, and their lifespan will be significantly reduced.
Diet
At the pet store, you can pick up ready-made food for a specific breed of aquarium fish. Some foods enhance the natural color, while others enhance immunity. There are separate products for predators and herbivorous fish.
Versatile options for carnivorous and omnivorous breeds are on sale. It is possible to purchase food for fry and crustaceans. All food is formulated on the basis of natural ingredients, does not provoke the growth of algae in the aquarium and contributes to the fast saturation of fish.

However, ready-made feeds are very high in calories, so the fish should not be overfeeded. Otherwise, some species die, others become obese. Even if the behavior of the fish does not portend trouble, you should pay attention to the state of the aquatic environment.
In case of overfeeding, the water quickly becomes cloudy after replacement, algae and the walls of the container are covered with a slippery coating. A film forms on the surface of the water, and the liquid smells unpleasantly rotten.
To avoid trouble, you should draw up a specific feeding schedule and strictly follow it. If there are small children in the family, you need to explain to them that fish are fed only at strictly defined hours.
Ideally, the feed should be eaten in a matter of minutes. If this does not happen, you should reconsider the diet of aquarium fish. Indeed, at each stage of development, each individual has its own requirements for food intake.

These recommendations may seem very troublesome, but in fact, all that is required from a novice aquarist is a responsible attitude towards their future pets. After all, every aquarium owner wants to be proud of his ability to grow and maintain beautiful bright fish.
How to prolong life?
Fish will live longer if the owner follows the simple rules for caring for them exactly. In particular, they relate to the regular cleaning of the aquarium, the timely removal of feed leftovers and the adherence to the feeding schedule.
Sick fish require timely treatment. To prevent an epidemic, sick individuals should be isolated from the aquarium and treated in a separate container. Live algae should be planted in the aquarium so that pets can hide and rest.


It is important to avoid overpopulation, otherwise the fish will be under constant stress. Many options for calculating the number of fish are considered controversial, therefore experts recommend starting from the capacity of the container and the size of the fish itself.
For example, fish up to 4 cm like cardinal, guppy, rassbora or neon will look good in an aquarium of 10 liters or more with a stocking density of 1 liter per fish. For 6-centimeter platies, thorns, hasemanias, rhodostomus, minor and barbus, a 20-liter container is suitable. Stocking density - 1.5 liters per individual.

Sword bearer, mollies, apistogram, cross, black barbus should be placed in an aquarium of 150 liters at the rate of 3-10 liters of water per fish. For larger goldfish, scalar and Malabar zebrafish, a 200 liter container is suitable. There are no specific rules for the number of fish, here it is important to take into account the nature of the individual itself.
Large fish such as cichlamosa, astronotus and akara are suitable for a volume of 250 liters (for a couple) or 500 for a flock. Discus require special conditions - they need an aquarium of 200 liters at the rate of 50 liters per individual.

The only fish that benefit from overpopulation are the Malawian cichlids - dense populations make them less aggressive. Bottom fish are not counted in total. If the capacity allows, you can put several catfish and battles in the aquarium. Up to 5 burrowing catfish and one sucker catfish can freely live in one container.

All the rules and recommendations discussed above will help the novice aquarist create his own underwater world and extend the life of its inhabitants.
See the following video for tips for novice aquarists.








