Artificial diamonds: what do they look like, how are they obtained and where are they used?

Diamonds stand out for their unique structure density, which allows the stone to withstand heavy loads and high temperatures. This property is used in space research and development, in the production of medical devices and precision watches, and in the nuclear industry. After cutting, the beautiful mineral turns into a diamond, which is highly valued by jewelers. Modern technologies make it possible to create it in artificial conditions, reducing the price without losing quality.

Peculiarities
For active use on an industrial scale, artificial diamonds have been produced since 1993. Their quality was so high that jewelers required special tests to determine the authenticity of the stones. For the average consumer, the difference was not obvious at all, so many companies began to use crystals to create luxurious jewelry.

In modern laboratories, several types of this synthetic stone are grown: cerussites, fabulites, rhinestones, ferroelectrics, moissanites. The most beautiful and cleanest cube of zirconium dioxide, which is called "cubic zirconia", is considered. It is used in many areas of industry and complements the collections of the Thomas Sabo and Pandora fashion houses.

Key features of cultured diamonds:
- low cost in comparison with natural stones (the price is 10-15 times less);
- ease of cutting;
- no hidden defects that affect hardness (air bubbles, cracks);
- full imitation of a real diamond after cutting.

Among lovers of beautiful stones, opinions were also divided about the properties of an unnatural stone. Some of them believe that only a real diamond is able to drive away evil spirits, protect its owner from damage and the evil eye, and help him in commercial affairs.
Imitation diamond owners claim that their jewelry is equally effective in emitting positive energy and bringing good luck.

Artificial stones have been developed in recent years by the well-known brands Diamond Foundry, Helzberg's Diamond Shops and LifeGem. This business in the United States is considered the most profitable and promising, since the harm to the environment is minimal. In addition, many geological experiments prove that the period of formation of diamonds in nature is over. Therefore, the development of new deposits will soon become a thing of the past.

Receipt history
Real diamonds have been popular for centuries. Expensive diamonds adorned royal clothes and crowns, were inherited and entered into the gold reserves of the treasury of many countries. Even today, faceted minerals are the best investment and only increase in value every year.
Therefore, the first developments and attempts to create a synthetic stone began at the end of the 19th century.

The first artificial diamond was obtained in 1950 by Swedish scientists at the ASEA laboratory. After research, their experience was repeated by the American company General Electric in 1956, improving the technology. Over the course of several decades, new methods and developments have appeared that have made it possible to change the shade, shape and size of a synthetic mineral. In 1967, a patent was obtained for the cultivation of gemstones.
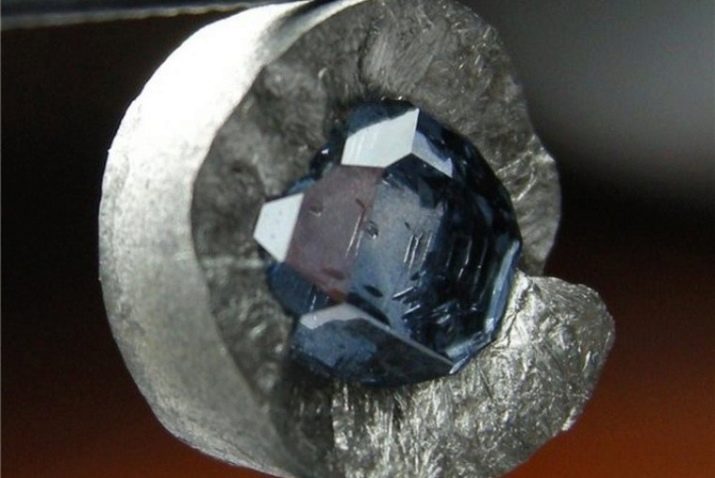

The history of their production in the Soviet Union begins with the first stone, which was synthesized at the Institute of Physics and High Pressure in the late 50s of the last century. But active work in this direction is carried out by the scientist OI Leipunsky, who published many scientific papers and calculations back in 1946.
His work in the field of chemistry was used as the basis for new methods, they practically became the basis for the modern industrial production of artificial diamonds.

A real breakthrough happened in the early 60s of the last century, when young scientists from the Moscow High Pressure Laboratory created a special press. With his help, it was possible to establish a large-scale production of heavy-duty stones: the volume reached a thousand carats per day. All industrial diamonds produced were used for the needs of rocketry and mechanical engineering, were exported, bringing billions in profits.

In recent years, new technologies have been developed in Russia by private jewelry houses and scientific laboratories.
They attract foreign experts from South Africa, the USA and Europe, trying to reduce the cost of the method.
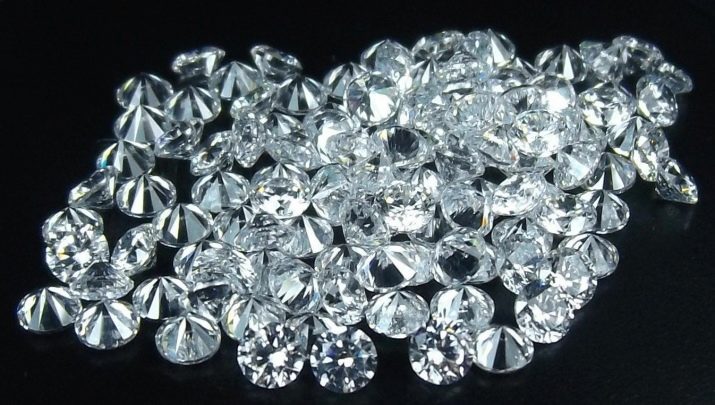

How are synthetic diamonds made?
Artificial diamonds grown in the laboratories of leading chemical companies are difficult to distinguish from real stones in terms of transparency and brightness. But all known methods require large investments and are laborious.
Therefore, the main task of scientists is to find the perfect balance between quality and production cost.

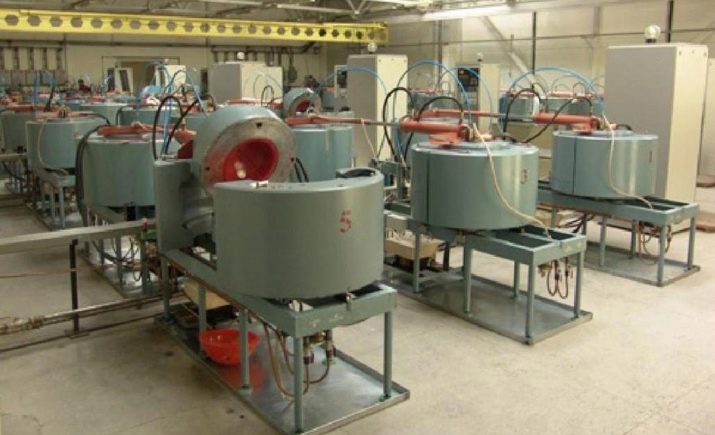
HPHT technique
HPHT or High Pressure, High Temperature is the most common technology. Scientists put real stones 0.5 mm in size in the basis of synthetic cubic zirconia. In a special chamber, according to the principle of operation, reminiscent of an autoclave, a combination of a temperature of at least 1400 ° C and a pressure of 55,000 atmospheres is created. Various chemical compounds and graphite layers are applied to the natural base.
After 10 days of such exposure, strong sigma bonds are formed, the joints around the base are formed into a hard and transparent stone.
This technology maximally recreates the natural conditions for the appearance of the mineral, so the quality is always at its best, defects are practically excluded.

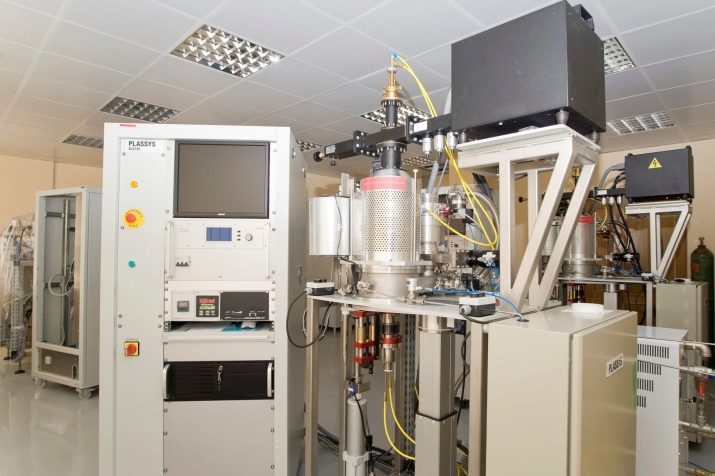
CVD production or film synthesis
This technology is one of the first in the cultivation of artificial minerals. It is widely used when it is necessary to create a particularly strong and sharp diamond coating, to create high-quality diamonds. All components and the diamond substrate are placed in special chambers that create a vacuum. After filling with methane, exposure to microwave rays, well known from the work of a microwave oven, begins. At high temperatures, chemical compounds of carbon begin to melt and combine with the base.

CVD technology produces high quality diamonds that are not inferior in properties to real ones. On their basis, a technology is being developed to replace wear-resistant computer boards, dielectrics and ultra-thin scalpels in ophthalmology.
Scientists hope that in the near future for 1 carat of synthetic stones obtained using this technology, it will be possible to reduce the price to 5–8 dollars.

Explosive synthesis technique
One of the latest developments is the explosive synthesis method. It is based on a combination of sharp heating of a chemical mixture using an explosion and subsequent freezing of the resulting mineral. The result is a naturally occurring synthetic diamond made from crystalline carbon. But the high cost makes chemists look for new options for the synthesis of stone mass.

Scope of application
Among all diamonds, synthetic stones occupy only 10% of the market. Inexpensive cubic zirconia crystals are used to make women's jewelry. Famous fashion houses decorate evening dresses, handbags and shoes with them, and use them in exclusive decor.
Progressive youth are increasingly choosing them for their safety and environmental friendliness.

More than 90% of artificial diamonds are used in industry. Main directions:
- high-precision grinding machines, tools for cutting hard materials;
- microelectronics and computer manufacturing;
- defense industry;
- robotics;
- unique lasers for eye surgery;
- mechanical engineering;
- new machine tools in metallurgy;
- rocket science.

Recent advances include the use of synthetic diamond to make an artificial lens. Transplant operations have shown that the clarity and ease of cut makes the implant ideal for the patient.
It has the right angle of refraction and durability.
Comparison with natural stones
The industry produces synthetic diamond, which is so similar to a natural crystal that a number of laboratory tests are required to identify it. Let's take a look at the most common differences.
- All artificially grown diamonds have a special stamp. It gives the name of the company or laboratory that produced the product.

- It is better to use a powerful microscope rather than a magnifying glass for inspection. In workshops, defects are detected using a spectrograph, and illuminated under ultraviolet rays.

- Real diamonds do not respond to electromagnetic fields. You can use this property as a test method: a synthetic stone is attracted to a strong magnet.
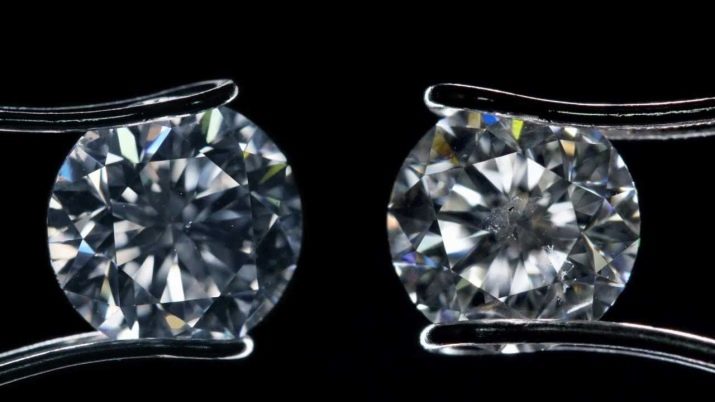

- If it is necessary to identify a diamond at home, it is placed on thick white paper. Close inspection reveals growth zones that arise when a layer of carbon is formed under high pressure.

- Natural stones are created from the smallest single crystals, therefore they have a homogeneous structure. When viewed in detail under a microscope, unnatural products seem to be composed of many microscopic crystals.

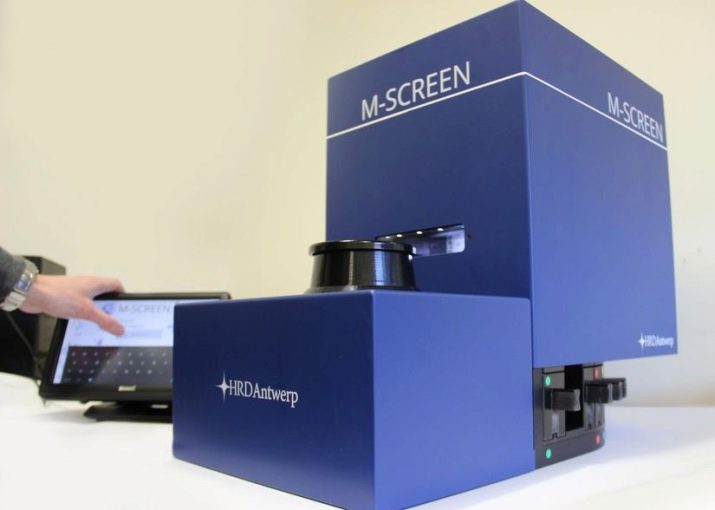
Diamond exchanges around the world use special Diamond Check and M-Screen instruments for analysis.
In just 10-15 seconds, they allow to distinguish synthetics from natural stone with an accuracy of 95-98%, give maximum information about the quality and structure of the crystal.


The production of synthetic diamonds is described in the next video.








