All about linen fabrics

Linen fabrics are distinguished by their natural composition, breathable structure, and pleasant texture. They are used by designers to create eco-friendly clothes, curtains and other products and have retained their popularity for centuries. You can understand what it is by studying the composition, description and properties of linen fabrics, their characteristics.

What it is?
Natural materials are the basis for a sustainable approach to wardrobe design. Linen fabric fully complies with these requirements. Its production today differs little from how canvases were made in antiquity. Plants are harvested with a combine, grind, leave the resulting straw in the field to separate the fibers of the trusts. Then, from this raw material, which has undergone mechanical processing, combed ribbons and threads are obtained, weaves of different densities and structures are woven.
Description of linen fabric fully reveals its properties. The surface of the canvas is smooth, with a slight dullness, and cool to the touch. Quality linen is always dense, but not too coarse.
Externally, textiles have a similarity with cotton, but the interweaving of the threads is more structured, with an uneven thickness of the threads. The material does not stretch at all; it shrinks when wet.

Other characteristics of the canvases include:
- pleasant texture;
- thermal conductivity;
- breathability;
- hypoallergenic;
- wrinkle.
Linen fabrics are completely natural, but they can also have synthetic additives that improve their properties. The materials in this group have many obvious advantages.

In addition to completely excluding the chemical processing of fibers from production processes, the advantages of flax include the following characteristics.
- Resistant to wear and tear. Even with intensive daily use, the material retains a strong bond of threads, no scuffs appear on it. The service life of products is calculated in decades.
- Effective appearance. Linen products are considered luxurious, respectable, and high-status. They are highly regarded for their aesthetics, the ability to form beautiful draperies.
- Comfort to wear. The material allows air to circulate freely, absorbs sweat, dries easily. Thermoregulation of the body is not disturbed, in any season it is comfortable and cool to wear clothes.
- Antistatic properties. Natural fibers do not generate static electricity. The fabric becomes dirty more slowly, dust settles on it less than on synthetics.
- Biological resistance... Flax does not promote the growth of fungi and other pathogenic microorganisms.
There are also disadvantages. It is difficult to cut and sew products from the material, since its edges are prone to shedding. The seams should be processed more carefully.
Another significant disadvantage is the increased rigidity of the material. But at the same time it perfectly holds its shape, it is suitable for the manufacture of furniture upholstery, complex draperies.

History
The first mentions of flax in Russia are found in the "Tale of Bygone Years". This craft (production of linen) was traditional for the Russian north. But the history of the canvas itself is even more ancient. Samples of fabrics were found during excavations in Egypt and Greece. There are references to the manufacture of such fabrics even in the Bible.
According to scientific research, the first such production was organized in India about 9000 years ago. Then they began to use durable fabric in Babylon, Ancient Egypt, and Asian countries. European manufacturers used their own technologies for the production of thin cambric linen. The material turned out to be much more refined, bleached, used for sewing underwear and bed linen.

The appearance of flax in Russia is associated with the Celtic tribes and the Greeks. By the 13th century, domestic manufactories were already carrying out the industrial production of such fabrics, organizing their supply abroad. The advent of mechanical processing of raw materials revolutionized the textile industry. Linen fell in price, but the quality remained truly decent.
Modern production is organized in most countries of the world. With the rise of fashion, the trend towards sustainability has taken on a special significance for linen. Large factories for the production of fabrics from it operate in Canada, Belgium, Italy, Russia and Eastern Europe.

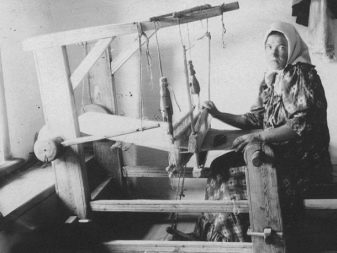
Views
Linen in rolls looks like a dense fabric with thick or thin threads intertwined. It has a recognizable structure and texture, can be covered with a light nap or have a glossy sheen. Material is classified according to several main characteristics.
By weaving method
Linen textiles are usually classified according to the method of weaving of threads. It directly defines how exactly the material can be applied. The following weave options are most common.
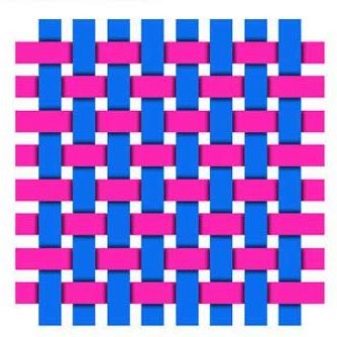
- Linen... It is characterized by an ordered arrangement of threads. Batiste, ravnduk have such a structure.

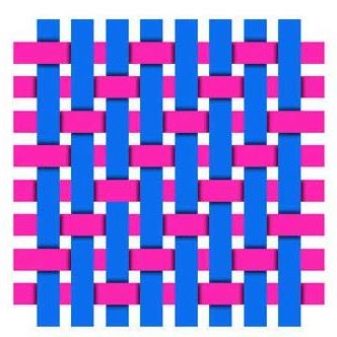
- Twill... With highly visible diagonal fibers. It features a high tensile strength.

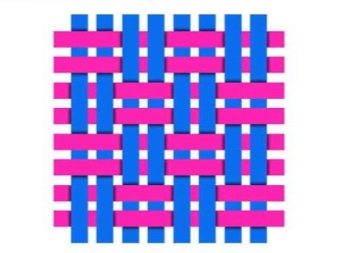
- Jacquard... Weaving with a large characteristic pattern. Has high strength, density, pronounced texture.
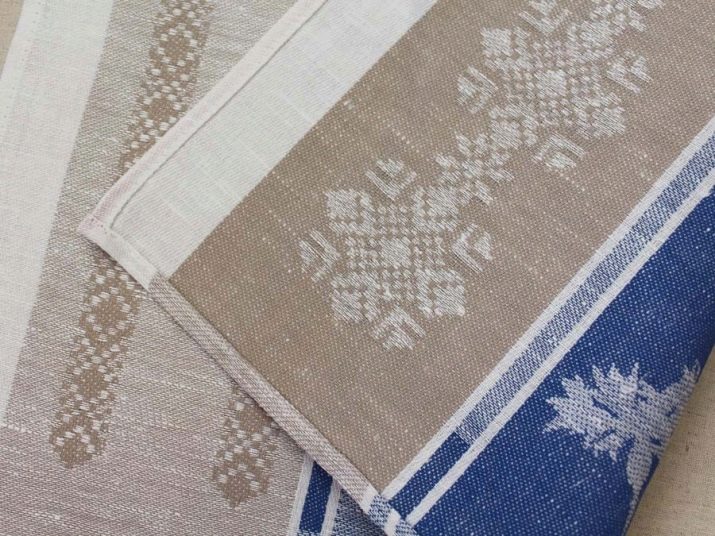

- Rogozhnoe... Patterned weave, rougher, but with a rather comfortable texture. The mat is considered as the main fabric for upholstery of upholstered furniture, wall decoration.

Linen fabric is also rare openwork weaving. Such textiles have decorative applications. Linen of satin weave is used to make kolomenok - an elegant fabric for ceremonial suits. The fibrous connection of the threads is typical for Damascus.


By composition
Natural linen is a material with constant characteristics. The addition of artificial or natural fibers can change the properties of the final product. This is how a linen stretch with good stretching properties, refined cambric and linen-quality damascus, similar to silk or viscose, is obtained. Also known are blended fabrics with cotton: visher, gauze, easy to iron, crease resistant, affordable.

The basic compositional classification rarely considers unique tissue varieties. Natural dense linen matting with a metal coating is popular among fashion designers. A mixture with viscose and lavsan is most often used to make twill, a material with a characteristic herringbone pattern on the surface.


By appointment
Linen fabrics are usually divided into several groups at once according to this criterion.
- Curtain... This includes types of curtain textiles, curtain fabrics that are well draped, dense and heavy.
- For towels. The most commonly used material is untreated and bleached, which absorbs moisture well.
- Canteens... Used to make tablecloths and napkins, and other serving utensils.
- Costume... Dense, smooth material that can hold its shape well. Not only suit pairs and triplets are sewn from it. The fabric is suitable for making other clothes: dresses, sundresses, overalls.
- Bed sheets... Used to create bed linen.
- Packaging... This category includes tarpaulin and other types of textiles that provide the creation of covers, carpets for various purposes.
- Terraced... Linen for technical use. Used to create artistic canvases, burlap.
- Embroidery... Canvas for intricate work, exquisite lace. Flax is used to make real works of art.
- Decorative or interior... Used for wall cladding, lampshades, furniture upholstery.
This is the main classification used by manufacturers and seamstresses, designers and textile suppliers.




Color spectrum
Linen fabrics are originally produced unbleached. They have a slight hairiness and a rather coarse texture. The color of the canvas turns out to be gray. The fabric acquires a white tint during the process of wearing. Industrial production also allows you to change the colors of the flax. When bleached, it acquires a uniformly light color, becomes thinner and softer, with a smooth surface.


Flax of the following types is also distinguished.
- Plain dyed... The fabric has only one color over the entire surface, it can be black, blue, khaki, red.
- Colored... Using 2 or more shades of threads in the canvas. This is how textiles with a checkered pattern, stripes, and jacquard are obtained.
- Printed... Fabrics with a pattern that is applied over a background canvas are named exactly like this. Printed coupon linen has patterns that decrease in scale from the edge of the fabric to its central part.
The main market share is occupied by products made of plain dyed and colored materials.



Top manufacturers
Linen is a material that is considered elite and expensive. Natural fibers are quite laborious in procurement and processing, therefore, only enterprises with an extensive technical base work with them on a large scale. In Russia today, TDL-Textile has such capacities with two enterprises in its asset: BKLMN in Kostroma and Yakovlevsky Flax Mill in Privolzhsk. Another company is Gavrilov-Yamskiy Tkach.


The Orsha Linen Mill, one of the leaders of the Eastern European market, and Orekhovsky, specializing in industrial canvases, operate in Belarus. In Vilnius, Lithuania, there is a company UAB A grupe that produces high-quality canvases. Italy is famous for its exclusive linen fabrics, which can be found at Manifattura Del Prato SRL and other brands. Greek fabric from the Lokimidis Textiles factory is considered no less in demand.


Applications
Linen is used to make household items, clothing, and other products, including technical and industrial ones.The material with an interesting structure attracts designers of boho or eco-style clothing. The following things can be sewn from linen.
- Overalls for workers. It will turn out to be wear-resistant, comfortable even with prolonged wear.
- Shoes... The upper part of the garments is made of fabrics with a coarse weave structure.
- Wickerwork. The threads are suitable for macrame, lace making.
- Technical textiles... On a linen basis, make durable tarpaulin, packaging and bags, awnings.
- Home textiles. This includes bedspreads, curtains, bedding and rugs, tablecloths and towels.
- Linens. It can be smooth, less often terry.
- Summer dresses, skirts, sundresses... They provide good thermoregulation of the body and are comfortable to wear.
- Children's wardrobe items.
- Beach accessories. Flax is used to make bags, hats, and other leisure products.
- Costumes... Trouser pairs with jackets, vests fully correspond to the trends of casual, safari, eco styles.



For flax, there are practically no restrictions on use. You can find many areas in which this natural material finds its application.
Nuances of care
Commercially processed linen practically does not shrink during washing. When sewing it yourself, the fabric can change its volume when it gets wet. Observance of simple maintenance rules will help to avoid shrinkage, as well as other negative consequences.
- Low temperature wash. At high temperatures, shrinkage is more intense. Unpainted linen can be washed at 80 degrees, colored linen - up to +60. Linen fabrics, products from them are loaded into the machine separately from other clothes, home textiles.
- Using mild detergents... Special gels with less rigidity than powders and capsules are suitable.
- Rinse thoroughly. It is advisable to add citric acid to the water, which has an emollient effect. Natural lemon juice additionally promotes better rinsing of synthetic detergents.
- Stretched dry... This avoids creases, creases.
- Shaking... Linen fabrics should be exposed to wet conditions. So the fibers are saturated with air, straightened.
- Steaming... It is used on unfinished fabrics. It is advisable to carry out the procedure on weight so that the matter is not sealed. Also, steaming can remove creases formed during wearing, improper drying.
- Whitening... It is required for things that have turned yellow or gray over time. Chlorine bleaches will not work, but you can use ammonia or turpentine and then hang things in the sun to enhance the effect.
- Starching... This procedure helps protect textiles from wrinkling.
- Storage... Outside the periods of use, things are placed in covers, paper bags. This will prevent the fibers from absorbing foreign odors.



You may also need to soften linen at home when washing bed linen and in the process of caring for other textiles. There are several ways to achieve the desired result. You can soften the wash water by adding baking soda: about 100 g per 10 liters. This will have a beneficial effect on the fabric itself.
Also, ordinary table salt helps to soften linen. A solution is prepared from 100 g of this substance and 10 liters of water, in which the products are soaked for 8-10 hours. After the laundry is rinsed out, washed as usual.
Dry garments and whole fabric cuts soften by crushing and squeezing, shaking and rubbing. The practice of twisting into bundles and braids is also used.










